 This is part 2 of my CAVA blog post series. In this post, I will go through common error messages you could see in the output of server_viruschk. For those of you haven’t already, please check out part 1 where I go line by line through the output of the server_viruscheck command.
This is part 2 of my CAVA blog post series. In this post, I will go through common error messages you could see in the output of server_viruschk. For those of you haven’t already, please check out part 1 where I go line by line through the output of the server_viruscheck command.
Most of these errors have to do with the account used for CAVA. This account is set as the “Log on as” option for EMC Cava in the “services” section of windows.
OBJECT_NAME_NOT_FOUND:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 OFFLINE at Sat Aug 20 20:28:33 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: , ntStatus: OBJECT_NAME_NOT_FOUND
AV Engine:
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
No signature date
Description: ntStatus: OBJECT_NAME_NOT_FOUND means that the cava service is not running on the server.
Solution: Start the EMC CAVA service under the services menu on the AV server.
ERROR_AUTH 5:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 5 at Sat Aug 20 21:00:10 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
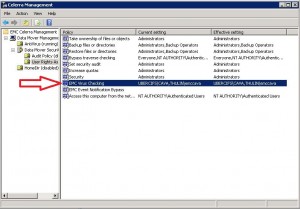 Description: ERROR_AUTH means that when cava when to connect to the “check$” folder on the cifs server, it ran into an error. In this case, ERROR_AUTH 5 means that the account does not have the viruschecking privilege.
Description: ERROR_AUTH means that when cava when to connect to the “check$” folder on the cifs server, it ran into an error. In this case, ERROR_AUTH 5 means that the account does not have the viruschecking privilege.
Resolution: Check to make sure that the EMC CAVA process is running under the cava network user and not the Local System account. If this is correct, verify that you gave the CAVA network account the Viruschecking Privilege in the MMC snap in.
AV_NOT_FOUND:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 AV_NOT_FOUND at Sat Aug 20 20:29:59 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Unknown third party antivirus software
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: AV_NOT_FOUND means that CAVA cannot find a running AV process. By default, cava uses a privilege called “Debug Program Rights” to search for the following applications running in memory: SpntSvc.exe, rtvscan.exe, Mcshield.exe, InoRT.exe, SWEEPSRV.SYS, SavService.exe, NTRtScan.exe, and kavfs.exe
Solution: First check to make sure your antivirus software is installed and running. If this is true, then make sure the CAVA account has the Debug Program Rights. By default, this privilege is granted to all local administrators, so add the cava account to the local administrators folder.
INVALID_PARAMETER:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 OFFLINE at Sun Aug 21 17:08:28 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: , ntStatus: INVALID_PARAMETER
AV Engine:
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
No signature date
Description: ntStatus is throwing an error trying to connect from the Cifs server to the Cava server. This error is caused when the CIFS server specified for CAVA is not joined to AD.
Resolution: Join the cifs server to AD and restart CAVA.
ERROR_AUTH 64:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 64 at Sun Aug 21 18:16:05 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: ERROR_AUTH 64 is because there is a kerberos skew error.
Resolution: Make sure the time on the cava server is within 5 minutes of the data mover.
ERROR_AUTH 86:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 86 at Sun Aug 21 17:25:31 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Problem: ERROR_AUTH 86 is caused when someone changes the password of the CAVA user in AD, but the cava software is using the old password.
Resolution: Update the password used for the cava account on each cava server. If you attempt to restart cava without updating, cava will fail to start with a logon failure error.
ERROR_AUTH 1265:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 1265 at Sun Aug 21 16:04:33 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: ERROR_AUTH 1265 is caused when the cava user account has expired in AD. You can verify this if you attempt to login to a remote desktop with the cava user’s credentials.
Resolution: Have a domain admin reset the CAVA account and change it to never expire to keep this problem from returning.
ERROR_AUTH 1326:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 1326 at Sun Aug 21 17:49:37 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: ERROR_AUTH 1326 occurs when the cava user’s password has expired in AD.
Resolution: Change the cava account password and have a domain admin set it to never expire.
ERROR_AUTH 1331:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 1331 at Sun Aug 21 17:09:45 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: ERROR_AUTH 1331 is when the cava account object is disabled or logon hours have been put in place to deny logon.
Resolution: Have a domain admin enable the cava account object in AD and confirm that the cava account can logon at all hours of the day.
ERROR_AUTH 1909:
server_2 :
10 threads started.
1 Checker IP Address(es):
192.168.1.101 ERROR_AUTH 1909 at Sun Aug 21 17:57:17 2011 (GMT-00:00)
MS-RPC over SMB, CAVA version: 4.8.5.0, ntStatus: SUCCESS
AV Engine: Symantec AV
Server Name: cava.thulin.local
Last time signature updated: Tue May 17 05:55:23 2011 (GMT-00:00)
Description: ERROR_AUTH 1909 occurs when the cava user account has been locked out due to too many invalid logon attempts.
Resolution: Have an AD admin reset the lockout status on the cava network user.
This should cover most of the common errors you will find when cava is running. You may have to check the server logs on cava to see them in the event that cava is turned off. If you have experienced a problem and my resolution does not fix it, please let me know and also open a case with EMC Celerra support.
On a side note, I want to also recognize Daniel Morris for his blog posts on CAVA. I urge you to read the following links to get a good understanding as well.
http://blog.planetchopstick.com/2010/10/18/what-is-emc-cava-celerra-anti-virus-agent/
http://blog.planetchopstick.com/2011/05/03/cava-considerations-and-basic-setup/
http://blog.planetchopstick.com/2011/05/05/cava-troubleshooting/
 As more and more people start to deploy a new VNX and switch to an advanced windows server operating system, I am seeing a higher utilization of the SMB2 protocol for cifs. With this increase, comes new problems. Recently I had noticed a rather peculiar notification in the server logs in regards to CAVA. CAVA was reporting the error “FILE_NOT_FOUND” on scans when the file existed. It would present itself as something like this:
As more and more people start to deploy a new VNX and switch to an advanced windows server operating system, I am seeing a higher utilization of the SMB2 protocol for cifs. With this increase, comes new problems. Recently I had noticed a rather peculiar notification in the server logs in regards to CAVA. CAVA was reporting the error “FILE_NOT_FOUND” on scans when the file existed. It would present itself as something like this:











 Twitter
Twitter LinkedIn
LinkedIn RSS
RSS Youtube
Youtube Picasa
Picasa Email
Email
